What is the Density Bonus Law?
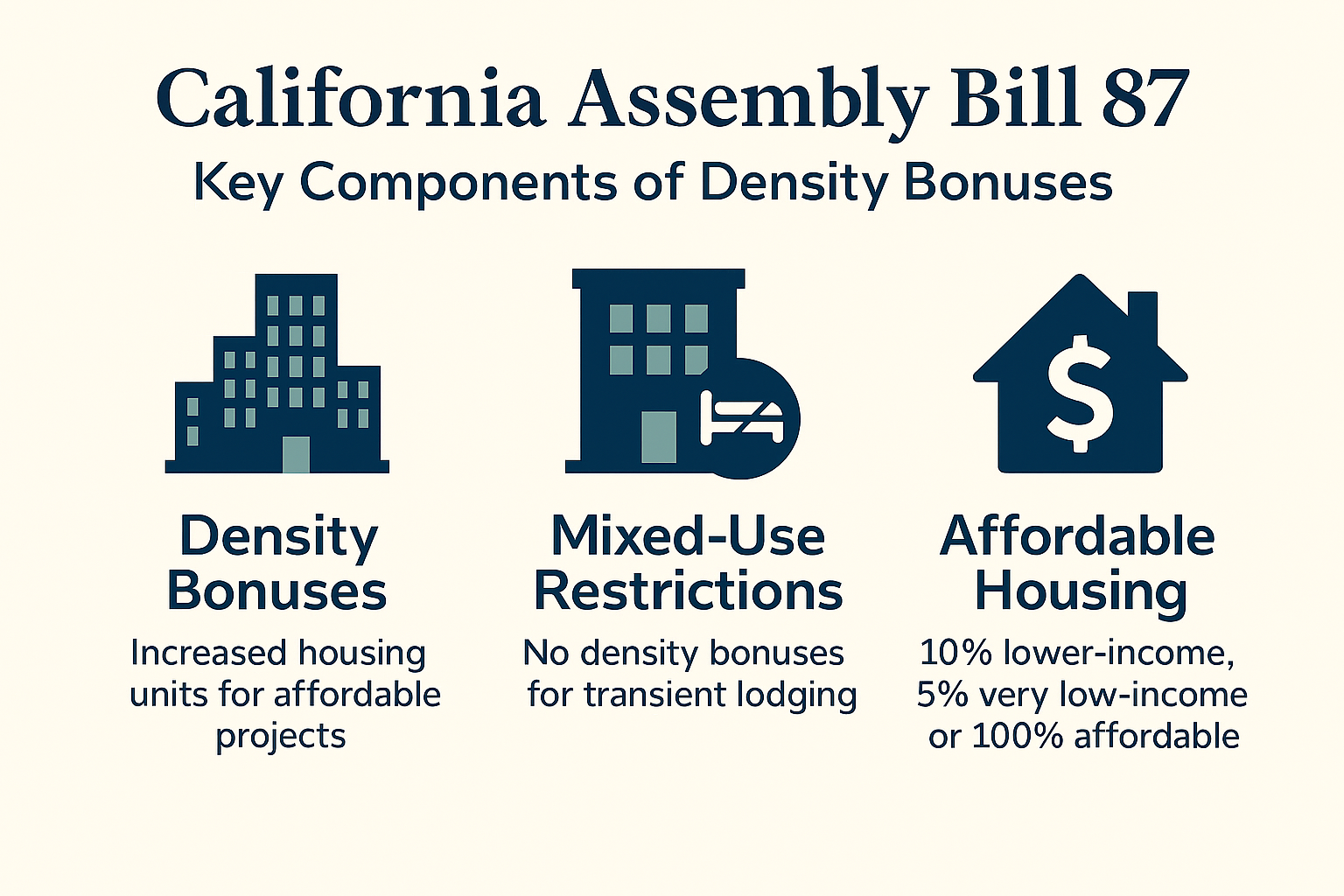
The Density Bonus Law (Government Code §65915) requires cities and counties to grant developers additional housing units—beyond local zoning limits—if they include affordable housing in their projects. Bonuses range from 20% to 50%, depending on the percentage and type of affordable units provided. For 100% affordable projects, bonuses can reach 80%, along with incentives like:
- Increased height limits
- Reduced parking requirements
- Modified development standards
Projects near major transit stops or in low-VMT areas may even qualify for unlimited density.
What AB 87 Changes
AB 87 clarifies that density bonuses and related concessions cannot apply to transient lodging—such as hotels, motels, or bed-and-breakfasts—within mixed-use developments. The bill ensures that DBL benefits remain focused on residential housing, not visitor-serving uses.
Key provisions:
- No incentives for hotel portions of mixed-use projects.
- Applies statewide, including charter cities, as a matter of statewide concern.
- Incorporates technical changes and aligns with other housing legislation (e.g., SB 92).
Affordable Housing Requirements Under DBL
To qualify for density bonuses, developers must include one or more of the following:
- 10% of units for lower-income households
- 5% for very low-income households
- 10% for moderate-income households in common interest developments
- 20% for lower-income students in student housing
- 100% affordable housing projects (with up to 20% moderate-income units allowed)
Impact of AB 87
- Focus on Housing Supply: Keeps DBL incentives targeted at residential development, preventing dilution by hotel or short-term lodging uses.
- Mixed-Use Development Clarity: Developers can still build mixed-use projects, but only the residential portion qualifies for density bonuses.
- AB 87: A Push for Affordable Housing in California
Criticism and Concerns
- Local Control: Some cities argue that this limits flexibility in planning mixed-use projects.
- Neighborhood Character: Critics worry about overdevelopment and strain on infrastructure.
- Implementation Challenges: Success depends on local governments adapting to new rules while striking a balance between community needs.
Why It Matters
AB 87: A Crucial Step in Addressing California’s Housing Crisis
Resources